




IN SEARCH OF LIFE
Go to this site: www.theguardians.com
Click on Microbiology on the navigation bar.
Click on "What is Microbiology"
What is Microbiology?
- What does micro mean?
- Make a long list of words which have the word micro in them.
- What does Biology mean?
- Name other words which have "ology" in the spelling. Give their meanings.
What sort of small, living things do microbiologists
study?
There are five different types of organisms (living things) bacteria, fungi, protists, archaea and algae. Each of these organisms does different things and is found in different places.
Who am I? Identify each organism from these clues.
- I can be on my own or one of many. I dont like dark places. I am green and I like to be wet in fresh or seawater which organism am I?
- I like the dark, I have a special substance which can eat organic matter. Some of us can make bread rise and some of us can be very poisonous. Our family grouped together has a special name. Which organism am I?
- I am a single celled organism. I have no middle (nucleus). I can be found everywhere on Earth and in some very unusual places. Which organism am I and name any unusual place where I can be found?
- You can find three different pictures of me as I may appear. I have a middle (nucleus) and I am sometimes mistaken for an ameba. Which organism am I?
- I am long and thin and my DNA floats freely in a cell. I can live in very hostile environments, such as salt lakes, hot springs, or in mid-ocean thermal vents. Which organism am I?
Create your own micro organism:
- What are its characteristics?
- Where does it live?
- What colour is it?
- Now draw a picture and write about how it was formed.
Story writing:
You are a micro organism. Are you a good organism or a bad organism?
Explain where you live and who you live with.
EG You are a friendly bacteria who lives with its family in the kitchen and you help protect the environment from bad organisms by eating them and keeping the family safe.
Mathematics
Bacteria come in many shapes - round, rod, comma, spiral and even square!
When joined together they can also take up a variety of shapes, such as clusters, chains, cubic packets, squares and bunches of grapes.
Activity 1 younge students
Choose one shape form the above list and one colour and using a drawing program on your computer draw some repeating patterns.
Activity 2 older students
Choose two shapes which will fit neatly together and using a drawing program on your computer, design some tesselations.
Activity 3 older students
If one bacteria landed on your sandwich how many bacteria would it take to cover the whole surface? Work out a computer model using a spreadsheet with variables which take into account the size of the slice of bread, the size of the bacteria and the rate of growth. Eg size of bread 10 x 10 cm (for a hungry giant!). Size of bacteria 0.003 mm, rate of growth doubles every time interval.
If your model works try it out on a bigger area such as how many bacteria would it take to colonise your bed, the school playground, the earth and the moon.
Activity 4 older students
Now create a model which shows what would happen if all five micro organisms were let loose on the earth to colonise freely. What would survive and what would die.
Write up your results and use graphs to illustrate your findings.
All microbes are bad for us, aren't they?
Click on the link RAINFOREST DISEASES.
 Activity
1
Activity
1
The mosquito transmits a disease called malaria. Find out what this disease is and how it affects humans. Are there any other diseases which are transmitted by animals or insects to humans?
Draw an 8 box storyboard showing how microbes from a mosquito get into humans. Call your work Marvin Mosquito Conquers the Human Body.
Activity 2
In the old days people died as a result of some of the diseases spread by microbes and bacteria. As we have advanced in medicine and technology we have stopped some of these diseases altogether and some we have made less life threatening.
Look at one of these periods in history and see what were the most common diseases of the time and what were their effects. What was done to improve health, has it changed over the years? Work in groups of four and produce a piece of display work. Use text and pictures.
Look back: 20 years in the 1980s
50 years in the 1950s
100 years in the 1900s
200 years in the 1800s
400 years in the 1600s
Activity 3
Reading for Understanding: Influenza
Read the passage about Influenza and answer the following questions:
- Influenza is another word for what?
- Influenza is most common amongst which population?
- Influenza mutates at an alarming rate and new strains appear on an annual basis. Look at the words in italics and try to explain what the writer is trying to say.
- Why do people in the northern hemisphere seem to get more influenza than people in the southern hemisphere?
- What are the best conditions for influenza to breed in?
- What does immune mean?
- Describe the symptoms of influenza.
- The passage states that the virus spreads quickly how does it do this?
- Where does most of the influenza originate and why?
- Draw a poster entitled Influenza can Kill and show the ways in which old people can look after themselves to prevent this illness.
- Draw a storyboard which could be used to teach young children about influenza, showing the different symptoms of the illness. Use a computer program to print up the text.
- Pretend you are an influenza virus write an account of the way you attack a human body. Make it as descriptive as possible.
Click on:- Some Famous Microbiologists and their Discoveries.
- Click on Bacteria and Archaea
- The work of Alice Catherine Evans led to the identification of what?
- What did her later research improve the treatment of?
- Who developed a system of classification for Group A Streptococcal Bacteria?
- What important method did Louis Pasteur develop in 1880?
- What does the term Virus mean?
- Name the lady who identified the cause of Whooping Cough?
- What did Alexander Fleming discover in 1928?
- What prize did he receive in1945?
Now research the list of Microbiologists and write about 5 more important discoveries. Produce a fact sheet about each discovery and put these into a class book - illustrate with drawings. Research how penicillin grows and start an experiment to plot the growth of these cells. Take pictures with a digital camera and write an account of the experiment using a word processor. Publish this on the Guardians Website.
Click on How do Microbes Work?
- Research the information about The Cell
- Write a few lines to describe the structure of a cell.
- What two types of cell structure exist?
Label the diagram below:-
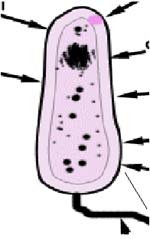
Prokaryote Cells
Write a sentence to describe the structure of the above cell?
Write an explanation of each of the terms listed below:-
- Chromosomes
- Ribosomes
- Cytoplasm
- Glycogen granules
Eukaroyte Cells
Write a sentence to describe the structure of the above cell?
Write an explanation of each of the terms listed below:-
- Nucleus
- Mitochondria
- Choroplasts
- Plastids
Go
to
Home
| Space
Station | Mars
| Rainforest
© 1999 Satellite Events Enterprises Inc.